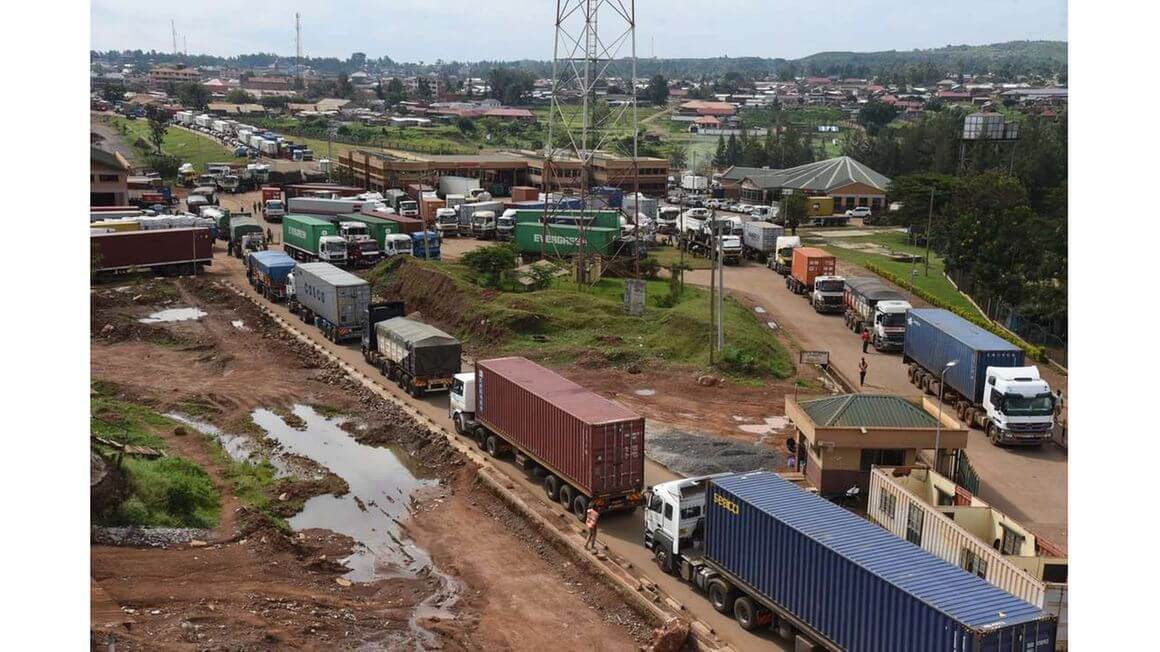
Sixty years since most African States attained independence, the Covid-19 pandemic has shone a fresh spotlight on the folly of the haphazard colonial boundaries. Long traffic jams at border posts across the continent, especially at the beginning of the pandemic, were the poster child of the non-tariff barriers that continue to hamper trade in Africa. These boundaries are the primary reason for the high cost of doing business in Africa and are the cause of low intra-African trade, investment, economic integration, and poverty. Covid-19 has also introduced a new economic paradigm, with digital technology taking the lead to ease the safe flow of goods across borders. If the pandemic persists late into 2021, some of the new digital technologies introduced to facilitate safe cross-border movement could become permanent fixtures across the continent and indeed other parts of the world. The concept of intra-African trade dates before the 15th century. Despite war and competitiveness among African empires, they traded among themselves, sometimes travelling long distances to do so. The Songhai Empire practically controlled the trans-Saharan trade whereby an array of goods and services including gold, slaves, ivory, silk, horses, and sugar were exchanged. As is the case today, trade was a mutual exchange of goods and services and it had two dimensions to it; commercial and societal. With increased trading activities came a well-developed system of trading. The barter trade system was eventually replaced by currencies such as coins used in northern Africa, brass rods used by the Tiv of Nigeria,...
Technology shatters restrictive colonial boundaries
Posted on: February 1, 2021
Posted on: February 1, 2021