Innovation in TMA Strategy 2
TMA Zambia Programme purposes to support the country to transform from a producer and exporter of primary products into a net exporter of value-added goods driven by modernised agriculture (with a focus on value addition), tourism and manufacturing. The trade and export focus show that Zambia’s national trade priorities include:
- Enhancing Policy and Regulatory Environment: Creation of an enabling policy environment that supports and sustains trade and export development;
- Product development: Developing new products and improving existing ones;
- Trade Support Network: Building capacity and enhancing the trade support network to ensure it responds to trade requirements;
- Market Penetration and Development: Securing of markets and supporting key identified products and services in these markets; and
- Trade Facilitation: Addressing trade facilitation-related constraints to improve the flow of goods and services.
TMA will adopt Zambia’s national priorities and anchor them same within the organisation project clusters of transport, logistics, trade facilitation, customs & tax, standards and NTBs. It will catalyse structural and policy changes to propel Zambia in achieving desired development outcomes, reduce poverty, create jobs, and make Zambia a prosperous middle-income country by 2030.
TMA will adopt Zambia’s national priorities and anchor them within the organisation project clusters of transport, logistics, trade facilitation, customs & tax, standards and NTBs. It will catalyse structural and policy changes to propel Zambia in achieving desired development outcomes, reduce poverty, create jobs, and make Zambia a prosperous middle-income country by 2030.
Programme Implementation.
Implementation will be in two phases.
Phase I:
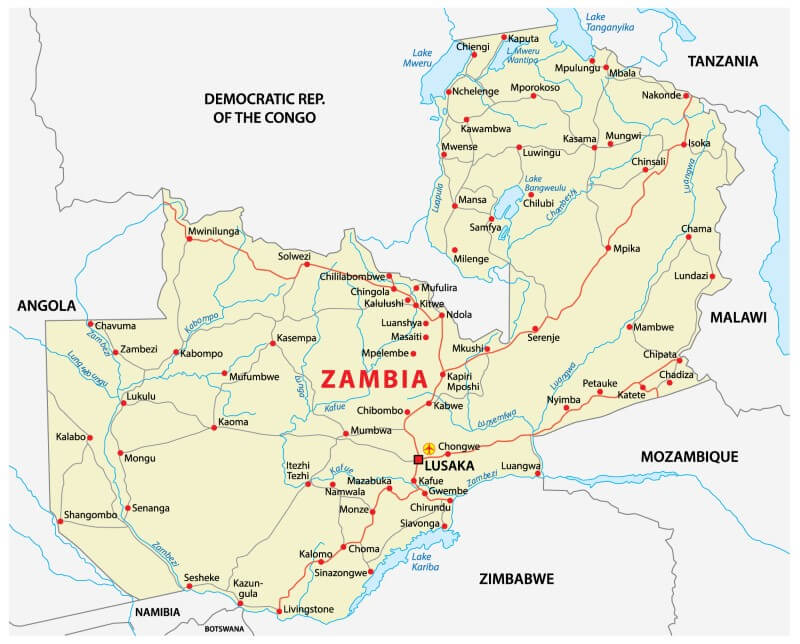
- Construction and operationalisation of the Nakonde OSBP, to complement our existing $7m investment in Tunduma on the Zambia-Tanzania border. This will include: upgrading the physical infrastructure and installation of IBM systems to enhance efficient clearance of cargo on the Zambian side
- Pilot a women cross border traders programme.
- Implementation of Safe Trade programme to mitigate impact on trade due to Covid-19 pandemic. Fundraising for longer-term funding for Phase II
Phase II
- Target Kasumbalesa and Mwami/Mchinji OSBPs amongst others that AfDB has requested for TMA’s partnership
- Develop cross border markets, cold storage facilities, specialised inland terminals and container depots.
- Enhanced trade and customs automation, standards & SPS, NTBs, logistics and export capability interventions.
- Mainstream public-private sector dialogue (PPD) for trade and investment throughout TMA’s project clusters.