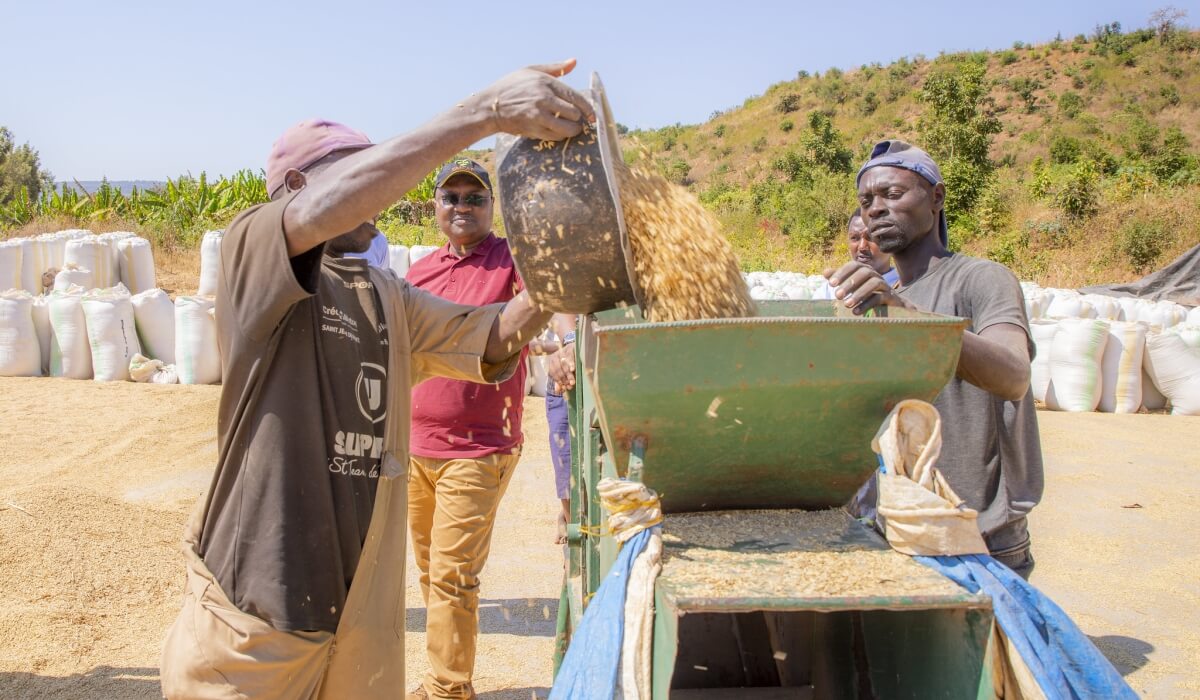
Three Rwandan small and medium-sized fresh produce companies recently showcased their products at the 2025 Fruit Logistica Expo in Berlin, Germany, making strides towards unlocking new opportunities in the export market. The exhibition, held from February 5–7, is one of the world’s largest trade fairs for the fresh produce industry. This year’s gathering brought together an estimated 66,000 visitors and 2,700 exhibitors from 145 countries, offering Kinvest Farms Company, Lotec Rwanda Ltd, and Effective M&N a global platform to promote their products, businesses, and prospect for new customers for their niche horticultural produce. Their participation was part of the five-year Value-added Initiative to Boost Employment (VIBE) programme that is implemented in Rwanda by TradeMark Africa (TMA), the International Trade Centre (ITC), in partnership with Mastercard Foundation. “Occasions such as this expo avail valuable opportunities for Rwanda’s fresh produce exporters to explore new markets, enhance their earning potential, and improve the prospects for other local enterprises to expand into European and global markets. By engaging directly with international stakeholders, these firms gained critical insights into market dynamics and established connections with potential buyers and strategic partners,” said Doreca Musenga, VIBE Programme at TradeMark Africa. The three companies, who are part of the many VIBE programme participants, collectively produce and export a variety of fresh produce, including French beans, passion fruits, chilies, snow peas, bird’s eye chilies, bananas, green chilies, habanero, and avocados. Despite their exponential potential, these firms, like many other micro, small and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs), face several challenges in...
Rwanda’s fresh produce enterprises seek new markets at global forums in Europe
Posted on: February 12, 2025
Posted on: February 12, 2025