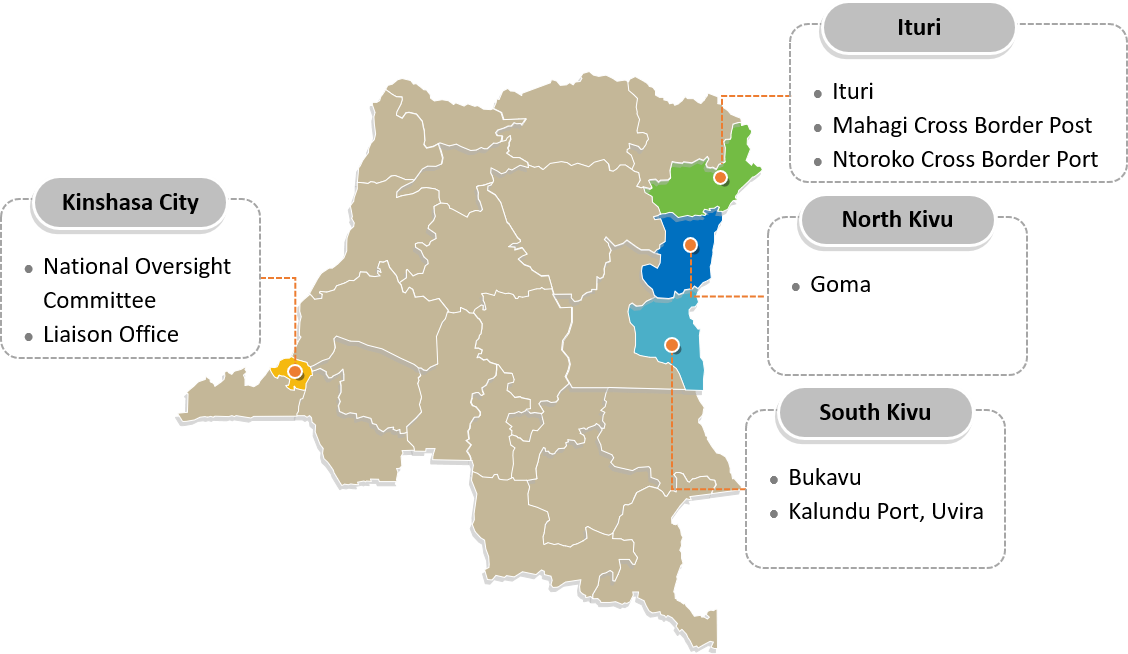
TMA has partnered with EAC governments bordering Congo and International community to roll out economic interventions along DRC and EAC borders. This will contribute to the creation of income-generating opportunities which will strengthen livelihoods for the people of Congo and their neighbours. Given, cross border trade between DRC and EAC is estimated at US$ 0.5 billion 2014, 50% of which is informal. This suggests that for sustainable change, interventions should promote both formal and informal trade. TMA project will target both formal and informal strands of trade; anchored on capacity building of traders, developing physical infrastructure, adoption of ICT and strengthening government institutional support. This is a sustainable way to lift citizens out of the cycle of poverty and offers potential for increased peace and stability along the borders, opening doors to improved livelihoods.
Current constraints to Cross Border Trade in Eastern DRC include:
- Poor roads and border infrastructure,
- Multiplication of border clearance processes leading to long delays at the border
- Lack of cross border trade information and knowledge
- Extortion, high taxes, multiple unofficial roadblocks
- Poor governance of border procedures.
- Harassment – Women traders across these borders are particularly at risk of sexual harassment including rape.