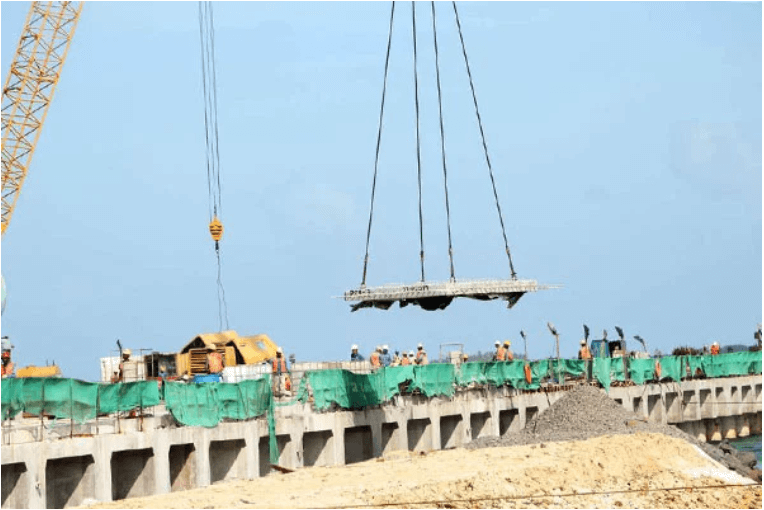
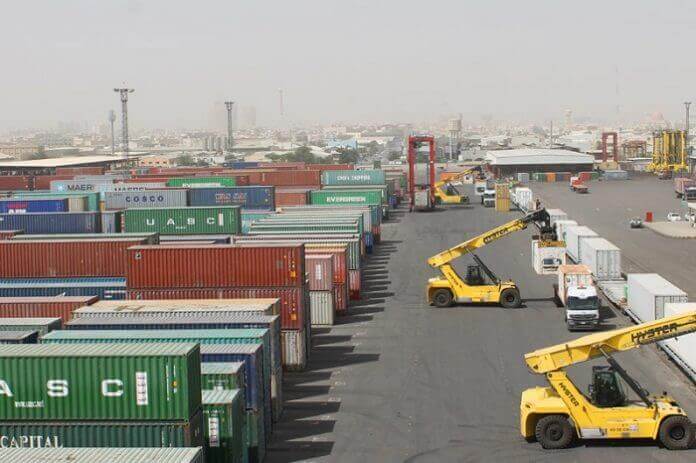
On May 30, 2019 Africa made history as the Agreement establishing the AfCFTA officially entered into force. With 54 out of the 55 member states of the African Union signing the agreement, Africa brought into being the largest trading block since the formation of the WTO. The entry into force of the AfCFTA is also marked by the speed at which African countries worked together within a year to establish a regional trading block to promote intra-African trade following the adoption of the AfCFTA on March 21, 2018 in Kigali, Rwanda. Following the ratification and entry into force of the AfCFTA, 5 supporting Operational Instruments were launched during the AU Summit held in Niamey, Niger in July 2019. These instruments are the key tools that will support the launch of the operational phase of the AfCFTA with start of trading scheduled for July 2020. The occasion also marked the announcement of the Republic of Ghana as the country to host the AfCFTA Secretariat. The operational instruments of the AfCFTA 1.The Rules of Origin: A regime governing the conditions under which a product or service can be traded duty free across the region. 2. The Tariff concessions: It has been agreed that there should be 90 per cent tariff liberalisation and the deadline is 1st July 2020. (Over a 10 year period with a 5 year transition, there will be an additional 7 per cent for “sensitive products” that must be liberalised). This will be supported by the AfCFTA Trade in Goods online portal...
The African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) enters into force
Posted on: October 29, 2019
Posted on: October 29, 2019



![The Africa Continental Free Trade Agreement…An Important Instrument For Ghana And Africa’s Economic Advancement [PART 1]](https://www.trademarkafrica.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/no-image.jpg)














