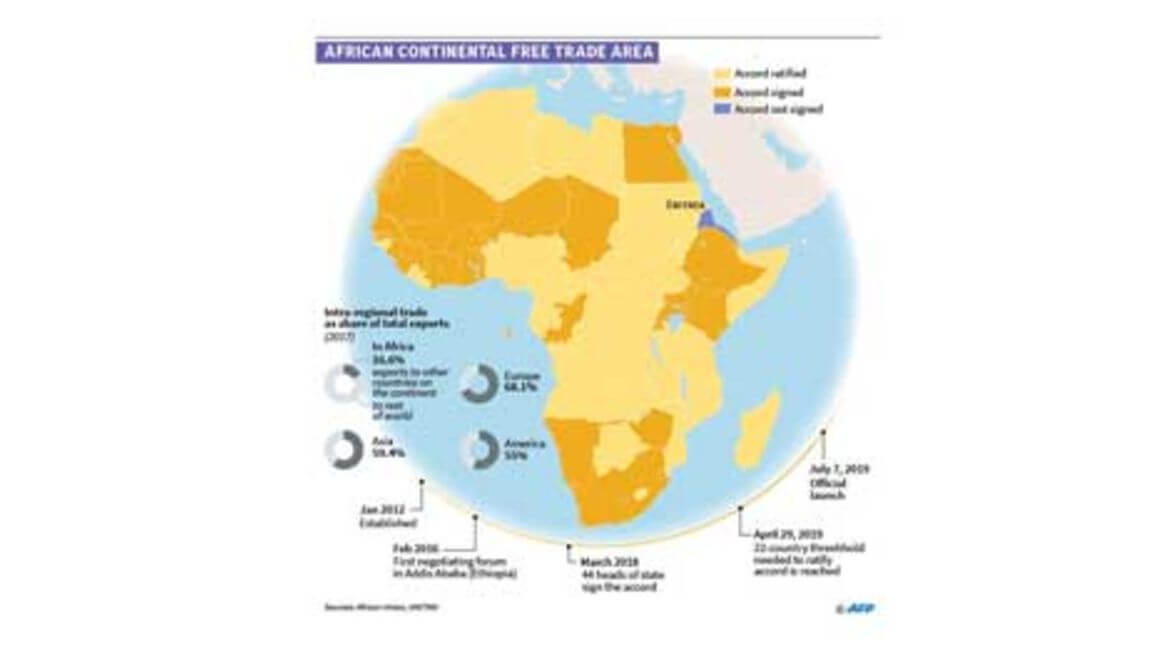
The official start of free trading under the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) in January 2021 moved a major continental aspiration closer to reality. One year later, cross-border trade in goods and services may not exactly be in full swing as had been anticipated, but indications are that there is some progress—the cup is half-full, not half-empty. A major hurdle is ongoing negotiations on the remaining crucial elements of the trade pact, particularly rules of origin. However, in an interview with Africa Renewal last month, the Secretary-General of the AfCFTA Secretariat, Wamkele Mene, sketched an optimistic vision of 2022. Factory workers producing garments for overseas clients, in Accra, Ghana. Credit: World Bank In sum, AfCFTA’s implementation will rev into higher gear, traders would be delighted, and the push toward accelerated industrialization of the continent should begin in earnest. Concluding negotiations on rules of origin, which is basically to determine the “nationalities” of thousands of products to prevent dumping, will be key to success. Already, negotiators have reached an impressive 87.8 percent agreement on rules of origin. That includes more than 80 percent of the about 8,000 products listed under the World Customs Organisation’s Harmonized System of rules of origin and tariffs. Such a high threshold of consensus guarantees that the vast majority of products can be traded. “What is outstanding are automobiles, textiles, clothing and sugar. These account for about 12-15 percent of what we call the tariff book. We want to conclude negotiations on these so that we can reach...
Key Pillars Mostly In Place To Speed Up Africa’s Free Trade In 2022
Posted on: January 24, 2022
Posted on: January 24, 2022